|
Hexagon Triplanar |
- Where to find it:
- Add Procedural Layer / Procedural / Extension Pack / Pattern /
 NodeGraph / Right Mouse Click / Add Nodes / Procedural / Extension Pack / Pattern /
NodeGraph / Right Mouse Click / Add Nodes / Procedural / Extension Pack / Pattern /
|
|
This Node is also available as a UV Tiling Version |
Hexagon Triplanar creates Hexagonal Patterns. Generation is done based on UV Space so there will be seams between tiles and uv shells.
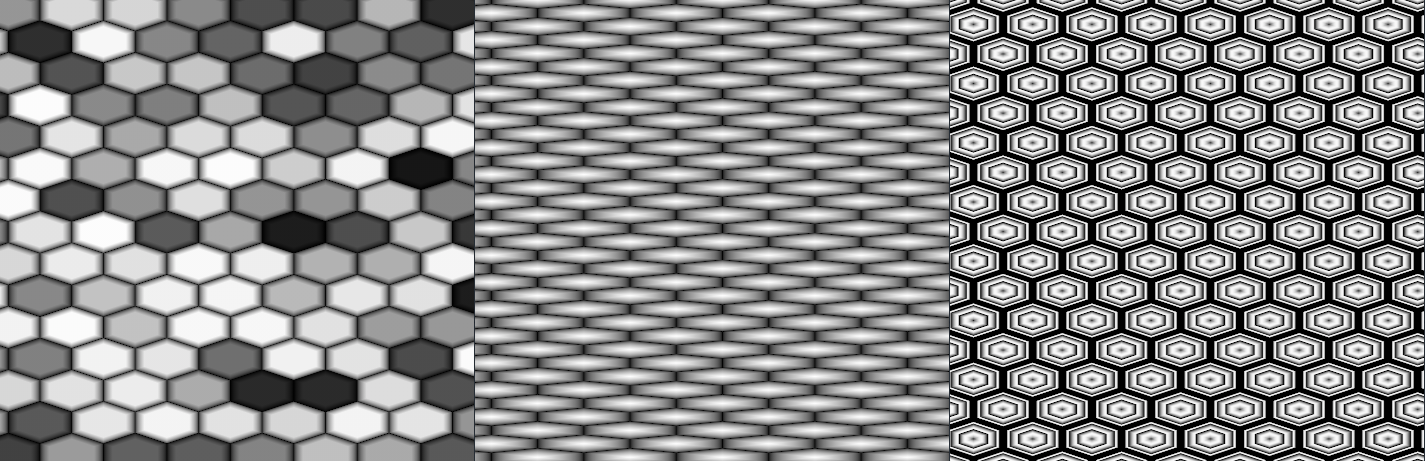
Some Examples produced with the Hexagon Node
|
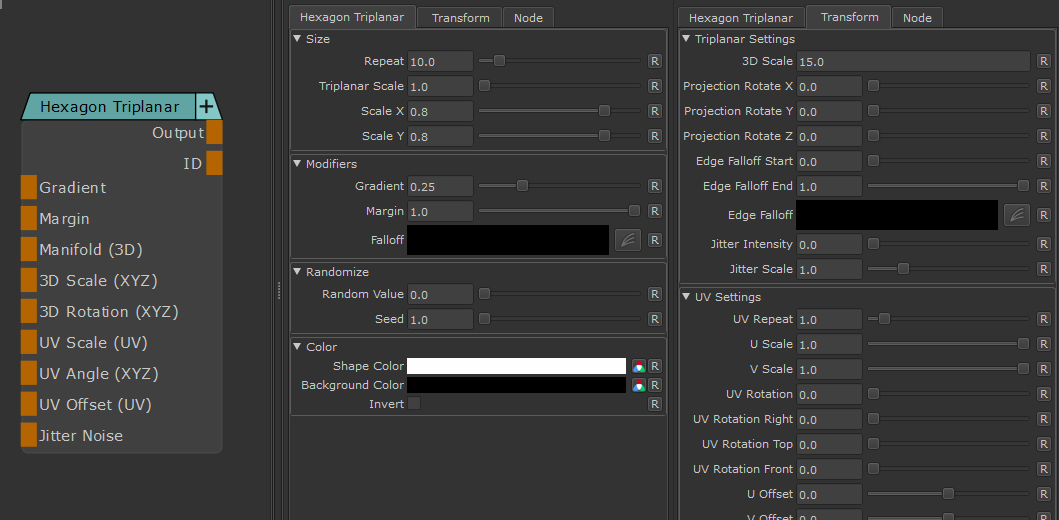
Node Overview |
|
Node Outputs |
- Output
Main Node Output
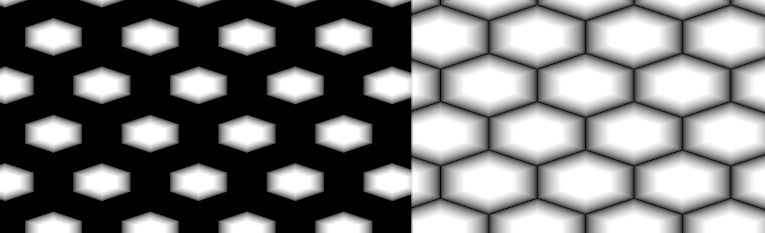
- ID
Outputs each Cell's ID as Grayscale Values
Example of Node Output (left) vs ID Output (right)

|
Node Ports |
- Gradient
Control the Gradient Amount within each Cell. Overwrites Gradient Slider
Example of different Gradient Values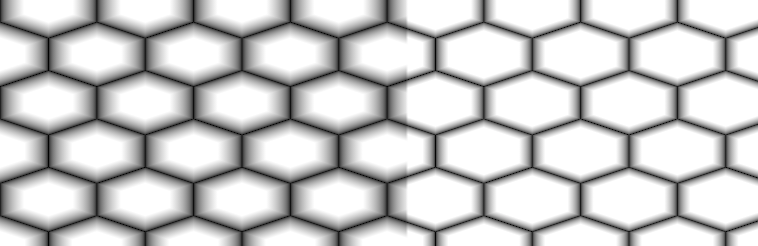
- Margin
Control the Gaps inbetween Cells. Overwrites Margin Slider
Example of different Margin Values
- Manifold 3D
When mapped the world space position the node uses to calculate the projection is supplied by the port.
This can be used for example to apply warping to the projection using Manifold Nodes
- 3D Scale (XYZ)
When mapped
- the red channel of the attached connection is used to drive the 3D Scale Attribute for the front part of the projection.
- The green channel of the attached connection is used to drive the 3D Scale Attribute for the top part of the projection.
- The blue channel of the attached connection is used to drive the 3D Scale Attribute for the right part of the projection.
- 3D Rotation (XYZ)
When mapped the red channel of the attached connection is used to drive the Rotate X Attribute,
the green channel the Rotate Y Attribute and the blue channel the Rotate Z Attribute
- UV Scale (UV)
When mapped the red channel of the attached connection is used to drive the UV Angle X Attribute,
the green channel the UV Angle Y Attribute and the blue channel the UV Angle Z Attribute
- UV Angle (XYZ)
When mapped the red channel of the attached connection is used to drive the UV Rotation Right Attribute,
the green channel the UV Rotation Top Attribute and the blue channel the UV Rotation Front Attribute
- UV Offset (UV)
When mapped the red channel of the attached connection is used to drive the U Offset Attribute,
the green channel the V Offset Attribute
By default the Edge Blending Jitter uses a node internal noise to perform its jittering/randomization of edges.
By attaching a noise of your choosing to the Jitter Noise Connection in the Nodegraph you can overwrite this
internal noise.

|
Node Properties |
MAIN TAB
|
Size |
- Repeat
Number of repeats of the Pattern
- Triplanar Scale
Scale of the Triplanar Projection. This is being multiplied by the 3D Scale Attribute in the Transform Tab of the Node
- Scale X / Y
Non Uniform Scale Factors of Cells in X and Y
Example of a non-uniform scale on the right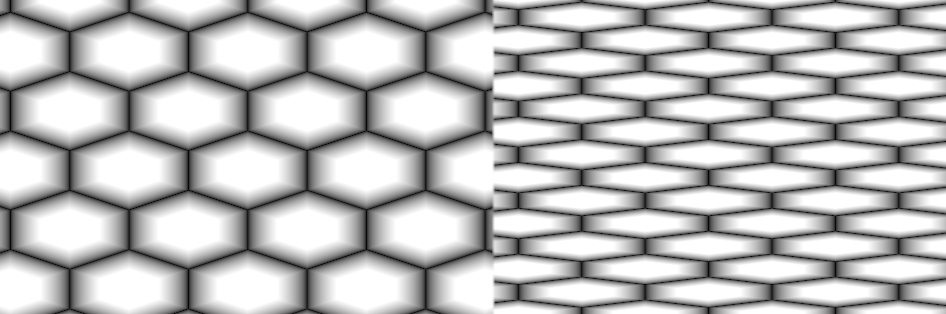
|
Modifiers |
- Gradient
Control the Gradient Amount within each Cell. Can be overwritten via a Node Input
Example of different Gradient Values
- Margin
Control the Gaps inbetween Cells. Overwrites Margin Slider
Example of different Margin Values

- Falloff
Remap Curve against the final result.
Example of different Falloff Curves applied to the same result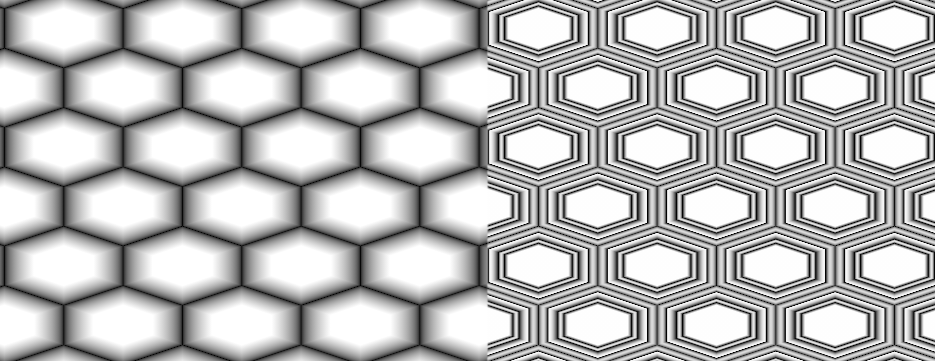
|
Randomize |
- Randomize Value
Blend Value to multiply Cell IDs against the result.
This can also be manually done by multiplying the two output ports of the Node (Output + ID) together.
Example of no randomization on the left, and randomization of 1.0 on the right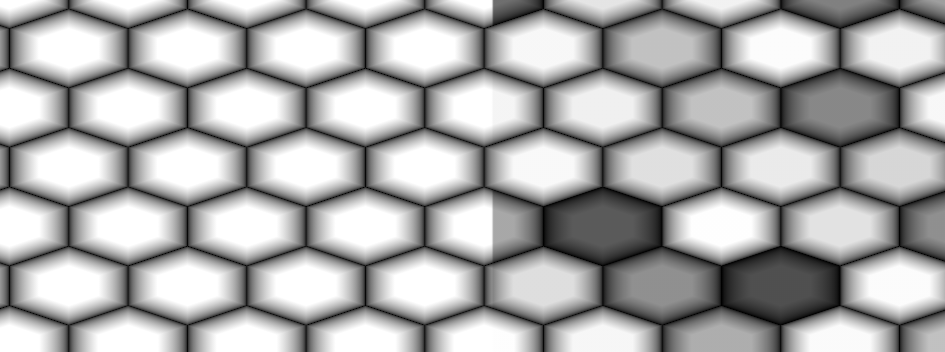
- Seed
Set the initial Start value of the IDs. This can be used to produce variations.
|
Color |
- Shape Color
Color of each cell
- Background Color
Color of area around cells.
- Invert
Reverse Shape and Background Color
TRANSFORM TAB
The Triplanar Settings control the projection in 3d Space
The settings are similar to a regular Triplanar Node found in Mari.
- 3D Scale
Will increase the size of the projection.
This is a very similar effect to changing the UV Repeat in the UV Settings.
- Projection Rotate X/Y/Z
Will change the rotation of the Triplanar 'Projection Cube' in space.
This should not be confused with changing UV Rotation which will rotate the projected image on
each side of the projection.
Projection Rotate is useful if your asset is not perfectly aligned in the main world space axis X Y and Z
and you see projection stretching as a result of it.
Sample of rotating a projection in 3d space. While this example is using
an Axis Projection Node the concept is the same for the Texture Scatter Triplanar Node

- Edge Falloff Start
The Edge Falloff Start determines the minimum angle where the projection
starts to be fully opaque
- Edge Falloff End
The Edge Falloff End determines the maximum angle where the projection
starts to be fully transparent
- Edge Falloff
The Edge Falloff Curve determines the general Falloff of each projection axis to its sides.
This is similar to adjusting the Edge Falloff Start and Edge Falloff End Sliders however
it allows you to create non-linear edge blending
Jitter will make the edges of projections less uniform/straight.
The Jitter Intensity determines the amplitude of the the Jitter.
You can overwrite the Noise used for jittering the edges by mapping the Jitter Noise Port in the Nodegraph

- Jitter Scale
Determines the Frequency of the internal Noise used for jittering.
|
|
Jitter Scale is ignored if something is attached via the Nodegraph to the Jitter Noise Port |
Will repeat the result x-amount of times. This is being multiplied with the repeat in the Main Tab
- U Scale
Will scale the result along U.
- V Scale
Will scale the result along V.
Will rotate the result for all axis of the Triplanar Projection
- UV Rotation Right
Will rotate the UVs just along the X-Axis of the Triplanar Projection.
- UV Rotation Top
Will rotate the UVs just along the Y-Axis of the Triplanar Projection.
- UV Rotation Front
Will rotate the UVs just along the Z-Axis of the Triplanar Projection.
- U Offset
Will offset the result along U.
- V Offset
Will offset the result along V.
