|
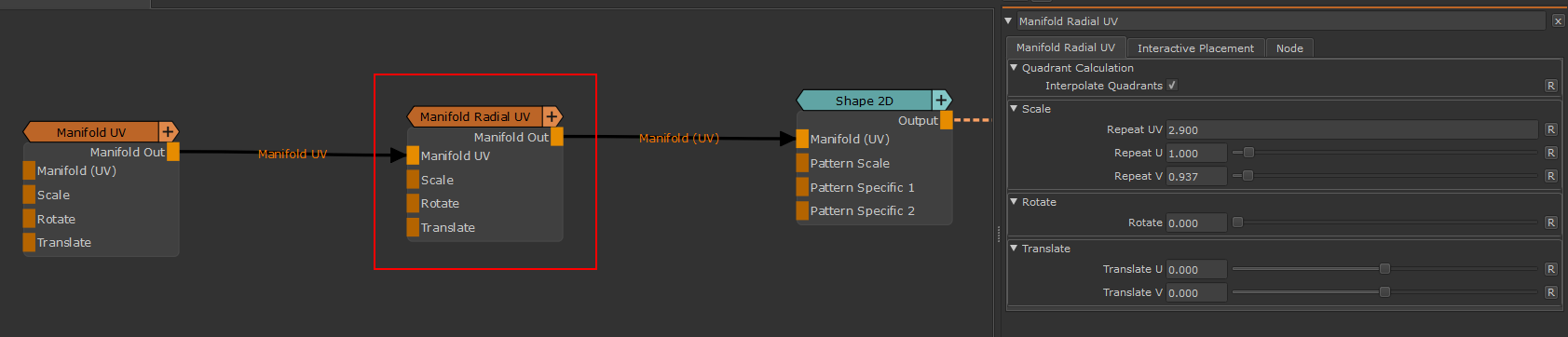
Manifold Radial UV |
- Where to find it: (This Node is available in the Nodegraph only)
 NodeGraph / Right Mouse Click / Add Nodes / Manifold /
NodeGraph / Right Mouse Click / Add Nodes / Manifold /
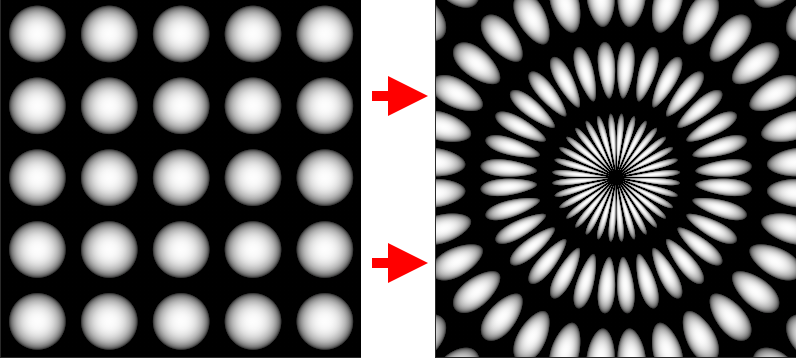
Manifold Radial UV can be used to convert patterns and images into a radial pattern by attaching it to the Manifold or UV Port of another Node.
|
Video |
For a complete tutorial on all Manifolds check here:
|
Node Overview |
Example of a Radial UV Node within a chain to convert a shape node to a radial shape
|
Node Ports |
- Manifold (UV)
When this connection is mapped in the Nodegraph it will overwrite the coordinate system used by the Node.
By default, if the 2D Coordinates Handle is unmapped the Node will use your Objects UV Data.
You can for example attach a 'UV' Node here or even another Manifold Node (Manifold UV, Manifold by Locator etc.)
- UV Scale (UV)
When this connection is mapped in the Nodegraph it will overwrite the Nodes Sliders in the Scale'
Group. You can attach any node to the Scale Handle and drive U and V by modifying the incoming RG(B)
Data (R = U, G = V, B = not used)
- UV Angle
When this connection is mapped in the Nodegraph it will overwrite the Nodes Sliders in the Rotate'
Group. You can attach any node to the Rotation Handle and drive U and V by modifying the incoming RG(B)
Data. Rotation is a 360 Degree Field so you need to modify the 'Intensity' of incoming values to get correct
degree numbers.
- UV Offset (UV)
When this connection is mapped in the Nodegraph it will overwrite the Nodes Sliders in the Translate'
Group. You can attach any node to the Translation Handle and drive U and V by modifying the incoming RG(B)
Data (R = U, G = V, B = not used)
|
Node Properties |
MAIN TAB
|
Quadrant Calculation |
- Interpolate Quadrants
This checkbox controls the algorithm used to 'fit' your uvs into a circle.
|
|
To find the best possible radial distribution experiment with this setting as well as the tiling of the Pattern the Node feeds into |

|
Transform Scale |
- Repeat UV
A global multiplier on the 'Repeat U' and Repeat V' Sliders. Changing the repeat in a Radial UV Node will change amount of 'Rings' generated.
- Repeat U
Sets the Repeat along the U coordinate (horizontal) multiplied by the 'Repeat UV'. Changing the repeat in a Radial UV Node will change amount of 'Rings' generated.
- Repeat V
Sets the Repeat along the V coordinate (vertical) multiplied by the 'Repeat UV'. Changing the repeat in a Radial UV Node will change amount of 'Rings' generated.
|
Transform Rotate |
- Rotate
Will apply a rotation to the UVs around the centre of them (u = 0.5,v = 0.5)
|
Transform Translate |
- Translate U / V
Will translate your UVs along U (horizontal) or V (vertical)
INTERACTIVE PLACEMENT TAB
|
Locators |
- Locator Translation Multiplier
UV Modifications are a 2D Process while Locator Movement in the Viewport is a 3D Process.
Moving your Locator a certain distance in the viewport might result in a faster or slower UV move than you are happy with.
The Locator Translation Multiplier is a multiplier against the distance you moved your locator in the viewport allowing you to fine tune
how much the UVs 'stick' to a locator movement.
|
|
By default your objects bounding boxes are used as a base for computation of movement. |
- Locator Translation
Allows you to pick or create a Locator for Translation so you can adjust the Manifold Transformations directly in the viewport.
Refer to the Locator Usage Section of the Manifold by Locator Node or the Locator Video above for samples.

|
Locator Axis Remap |
- X / Y / Z
Determines the mapping of each axis of the locator in the viewport to the node internal coordinate system.
UV Modifications are a 2D Process however the Locator movement in the viewport is a 3D Process.
Your UVs might rotated or your object's faces are aligned in the viewport in a way the default interpretation of a Locator Axis might not
correspond with your actual UVs anymore.
In these cases it might be necessary to change to the Axis mapping in order for Locator Modifications in the Viewport to affect the UVs in a more intuitive way.
- Invert X / Y / Z
Will invert the selected Axis. This can be useful for example in case of rotated UVs where a viewport locator move upwards moves the uvs downwards.
